Currency
📝 Introduction
The Currency function is an essential tool within your financial management system, designed to facilitate the handling and reporting of various currencies used in financial transactions. It provides a structured way to manage and maintain currency-related information, ensuring accuracy and consistency across all financial operations.
Once the list of currencies to be used for journal entries is set up, the next step is to configure the exchange rate table. This will allow for automatic conversion of values during journal entries.
🛠️ Usage
The primary purpose of the Currency function is to manage different currencies, their units, and their corresponding accounts, which are critical for accurate financial reporting and analysis. By using this function, organizations can easily handle multiple currencies, set up accounts for realized and non-realized gains and losses, and ensure compliance with international accounting standards.
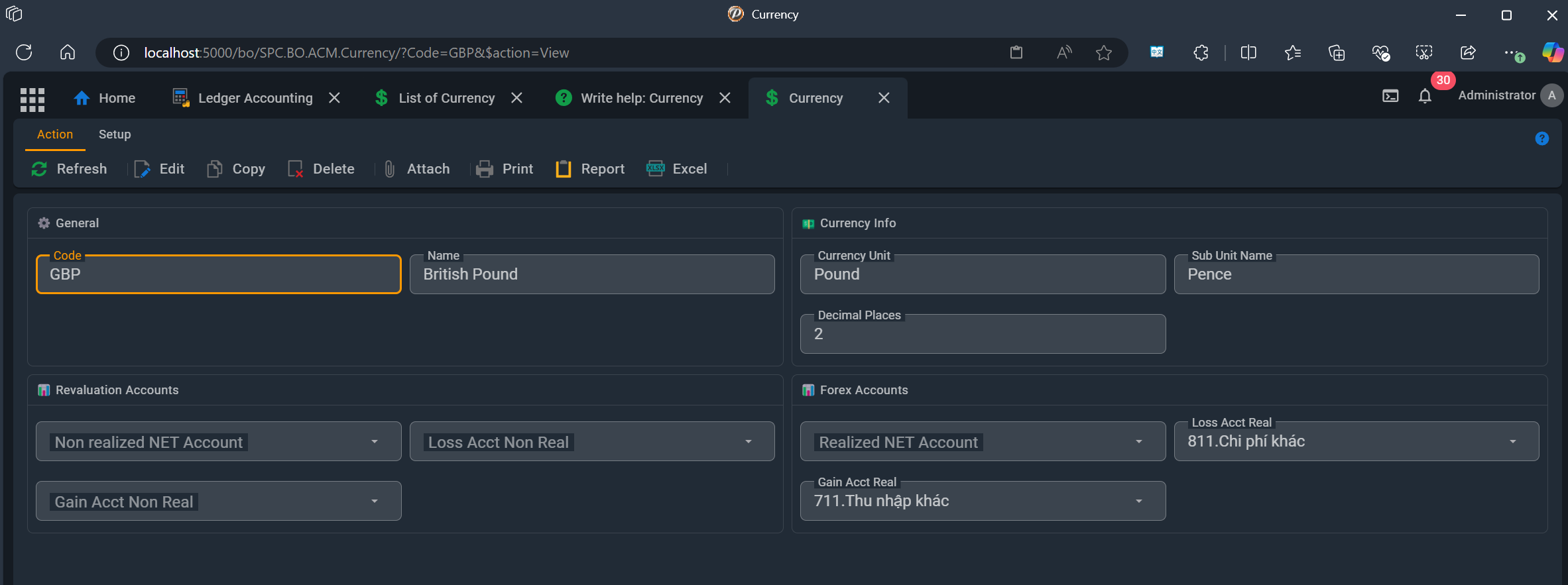
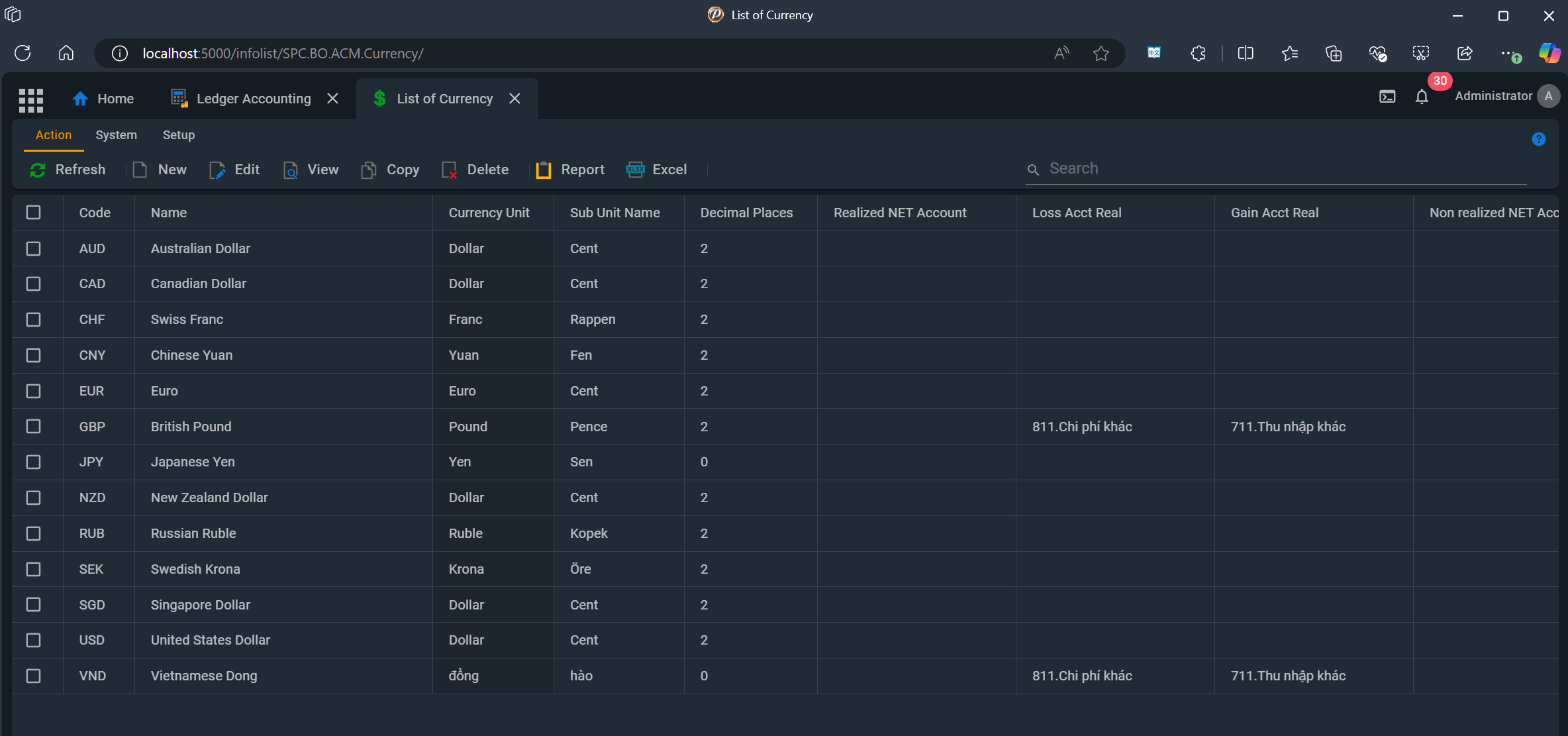
🏷️ Data Fields
General
- 🔑❗Code
- Enter the currency code (e.g., USD, EUR). Each currency is assigned a unique code (e.g., USD, EUR) to ensure clear identification and classification.
- 📝 Name
- Enter the name of this currency
Currency Info
- 📝 CurrUnitName
- Name of currency unit (e.g. dollar, dinar)
- 📝 SubUnitName
- Name of currency suv unit
- 📝 DecimalPlace
- Enter the name of this currency
Forex Accounts
- 📝 NetAcctReal 🔗 Chart of Accounts
- Select account for realized profit/loss
- 📝 LossAcctReal 🔗 Chart of Accounts
- Select account for realized loss
- 📝 GainAcctReal 🔗 Chart of Accounts
- Select account for realized profit
Revaluation Accounts
- 📝 NetAcctNonReal 🔗 Chart of Accounts
- 📝 LossAcctNonReal 🔗 Chart of Accounts
- 📝 GainAcctNonReal 🔗 Chart of Accounts
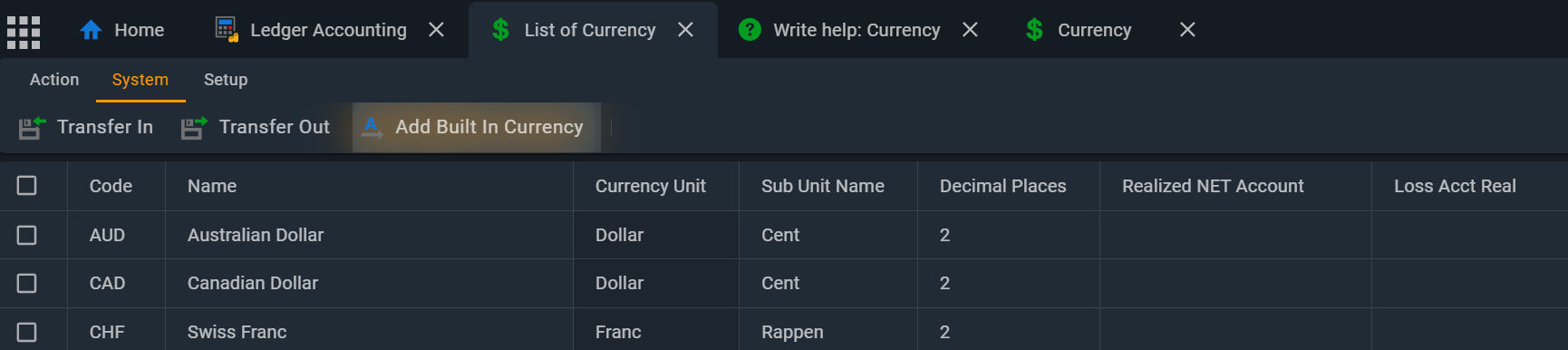
🔧 Download built in currency
Phoebus includes a list of the most commonly used currencies, which users can easily download to their data store. Additionally, users have the option to manually enter other currencies or copy and paste them from other sources.
Revaluation at Period End
Revaluation involves adjusting the book values of assets in other currencies to their fair market value. This ensures that the balance sheet reflects current market conditions.
At the end of the period, make adjustment entries to account for any unrealized gains or losses due to exchange rate movements.
For example, if a company holds cash in foreign currency, the value of this cash must be adjusted based on the prevailing exchange rates at the end of the period.
Forex Calculation for Matching Receivables and Payables
Forex (Foreign Exchange) Calculation for Matching Receivables and Payables is a critical process for companies dealing in multiple currencies. This involves calculating and matching the foreign exchange gains and losses associated with receivables (amounts owed to the company) and payables (amounts the company owes) in different currencies.
Calculating Forex Gains and Losses:
Forex Gains: If the exchange rate at the time of settlement is more favorable than the rate at the time of transaction, a forex gain is realized.
Forex Losses: If the exchange rate at the time of settlement is less favorable, a forex loss is incurred.
Forex accounts settings in this function make automatic posting Forex gain and loss possible. Match the receivables and payables with their corresponding forex calculations. Ensure that any differences due to exchange rate fluctuations are recorded in the appropriate accounts (e.g., forex gain or loss accounts).
These gains and losses must be calculated and recorded accurately to reflect their impact on the financial statements.
⚠️ Importance
Accurate Financial Reporting: Ensures that the company's financial statements reflect the true financial position and performance, considering the impact of foreign exchange rate fluctuations.
Compliance: Helps in adhering to accounting standards and regulations that require accurate recording of forex gains and losses.
Risk Management: Provides insights into the financial risks associated with currency fluctuations, enabling better risk management and decision-making.
By effectively managing evaluation at period end and forex calculations for matching receivables and payables, companies can maintain accurate financial records, comply with regulatory requirements, and manage financial risks associated with currency fluctuations.